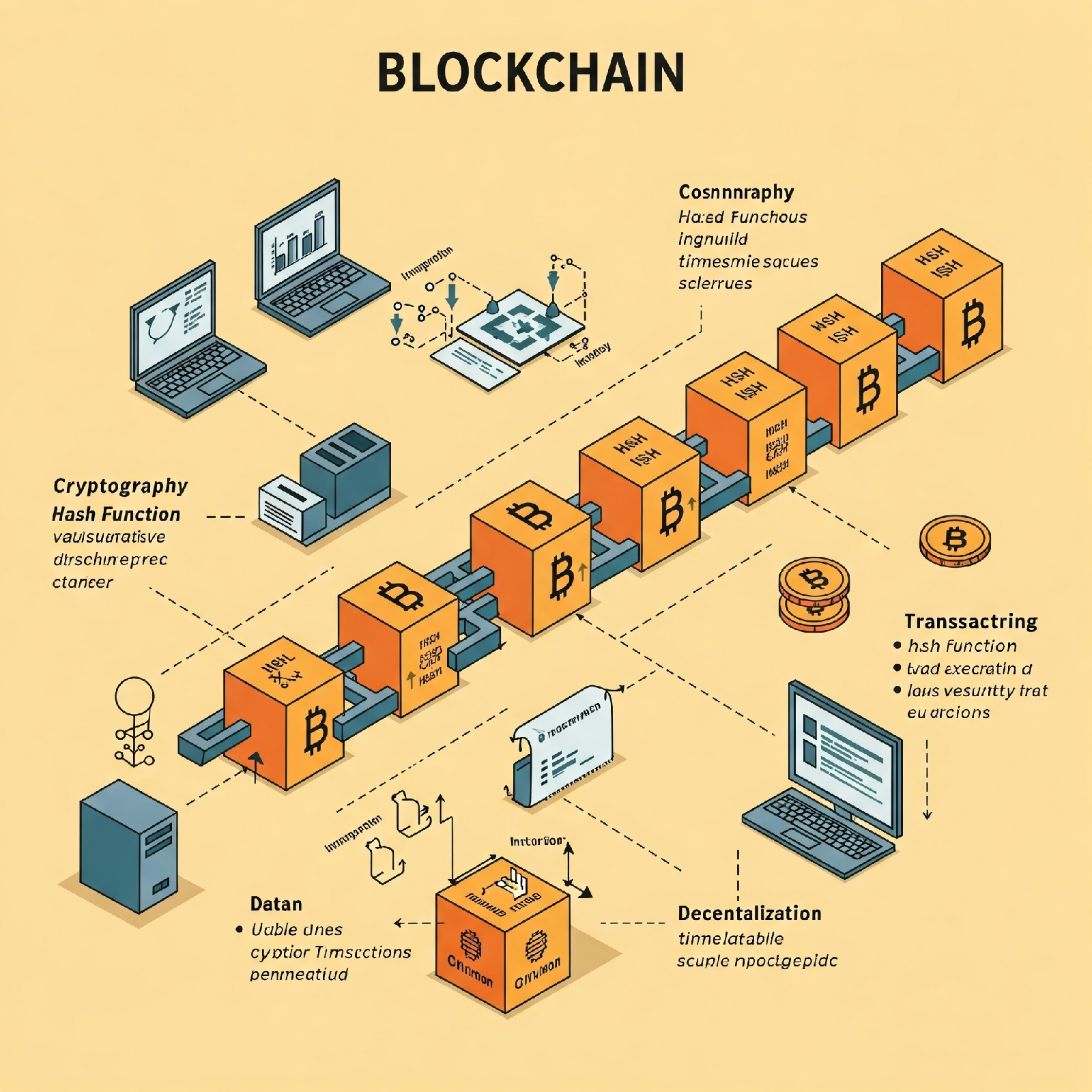
Blockchain is a decentralized, distributed, and often public digital ledger that records transactions across many computers. Think of it as a shared, constantly updated, and tamper-proof record book where each new entry ("block") is linked to the previous one using cryptography, forming a "chain."
Here's a breakdown of the key concepts:
* Blocks: Transactions are grouped into blocks. Each block contains a timestamp and a unique cryptographic code called a "hash," as well as the hash of the previous block in the chain.
* Chain: These blocks are linked chronologically and securely using cryptography. This linking makes it incredibly difficult to alter any information in past blocks without invalidating all subsequent blocks.
* Decentralized: Instead of being stored in one central location, the blockchain is distributed across a network of computers (nodes). This means no single entity controls the data, making it more resistant to censorship and single points of failure.
* Distributed Ledger: Every participant in the network typically has a copy of the blockchain, providing transparency and allowing for independent verification of transactions.
* Immutability: Once a block is added to the chain, it becomes very difficult to alter or delete it because doing so would require changing the hashes of that block and all subsequent blocks, as well as gaining consensus from the majority of the network.
* Consensus Mechanism: To ensure the validity of transactions and the integrity of the blockchain, network participants follow a set of rules called a consensus mechanism (e.g., Proof-of-Work, Proof-of-Stake) to agree on and validate new blocks before they are added to the chain.
* Transparency: Depending on whether it's a public or private blockchain, transaction data is often viewable to all or authorized participants on the network. However, the identities of the participants might be anonymized or pseudonymized.
Why is it important?
Blockchain technology offers several potential benefits, including:
* Enhanced Security: The decentralized and cryptographic nature makes it very difficult to tamper with data.
* Increased Transparency: All participants can often view the transaction history.
* Improved Efficiency: It can streamline processes by removing the need for intermediaries.
* Greater Trust: The distributed and immutable nature builds trust among participants.
* Cost Reduction: By eliminating intermediaries and automating processes, it can lower transaction costs.
Applications of Blockchain:
While often associated with cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin, blockchain technology has a wide range of potential applications across various industries, including:
* Finance: Secure and faster payments, cross-border transfers, digital currencies, decentralized finance (DeFi).
* Supply Chain Management: Tracking goods, ensuring transparency, verifying authenticity.
* Healthcare: Securely storing and sharing patient records, tracking pharmaceuticals.
* Digital Identity: Creating secure and self-sovereign digital identities.
* Voting Systems: Enhancing the security and transparency of elections.
* Intellectual Property Protection: Tracking ownership and usage of digital assets.
* Real Estate: Streamlining property transactions and maintaining secure records.
* Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs): Representing ownership of unique digital or physical assets.
In essence, blockchain provides a secure and transparent way to record and share data, fostering trust and efficiency in various applications.



Comments